| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |review |
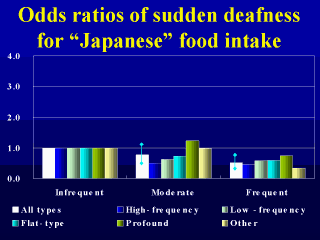 |
In regard to all
types, people who frequently consumed Japanese foods were only about half (OR=0.52, 95%
CI=0.33-0.82) as likely to be cases as people who infrequently consumed these foods. In hearing loss subgroups, people who frequently consumed Japanese foods were only about one-third (OR=0.34, 95% CI=0.12-0.95) as likely as those who infrequently consumed these foods to be cases with "other" hearing loss. In other four subgroups, people who frequently consumed Japanese foods had odds ratios less than one (ranging from 0.46 to 0.75), but again, the differences between these odds ratios and their respective reference groups were not statistically significant. |