Search inside of Supercourse and lectures in HTML and PPT format
 |
 |
front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |review |
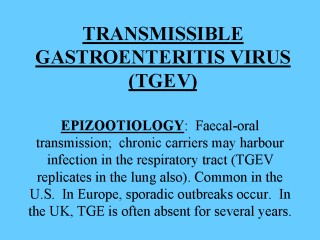 The disease occurs as two forms: Epizootic: Infection follows the entrance of virus into a non-immune herd. Symptoms develop very quickly and the disease spreads very rapidly (explosive infection). Older animals show anorexia, lethargy, diarrhoea, weight loss and vomiting. They recover in 1 week but in very young animals, mortality approaches 100%. Enzootic: The herd is persistently infected. Immune sows provide lactogenic immunity (IgA in milk) to the sucklings. Animals often have diarrhoea 1-2 weeks after weaning as maternally derived antibody declines. Clinical signs are similar but less severe than fully susceptible pigs. Similar pattern to rotavirus infection. |