Search inside of Supercourse and lectures in HTML and PPT format
 |
 |
front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |review |
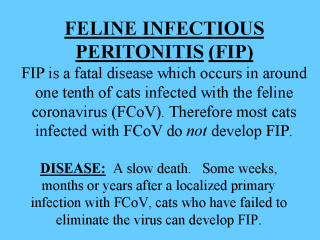 Three forms are recognised: Effusive (wet): Typical symptoms are chronic weight loss, depression, anorexia, fever and progressive abdominal enlargement caused by peritoneal and/or pleural effusions - fluid is clear to slightly opaque and very viscous with fibrin strands and often clots when exposed to air. There may be small necrotic lesions on the peritoneum and pleural surfaces. Non-effusive (dry): Clinical signs are more variable making this difficult to diagnose. Most have ocular abnormalities (eg corneal precipitates, bleeding into front of eye, iritis, colour change of iris) Disseminated pyogranulomatous lesions are found in major organ(s) - kidneys, liver, CNS, eyes. If a cat is ill and the reason is difficult to determine, dry FIP should be suspected. Combinations of effusive and non-effusive. |