| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35|36 |37 |38 |39 |40 |41 |42 |43 |44 |45 |46 |47 |48 |49 |50 |51 |52 |53 |54 |55 |56 |57 |58 |review |
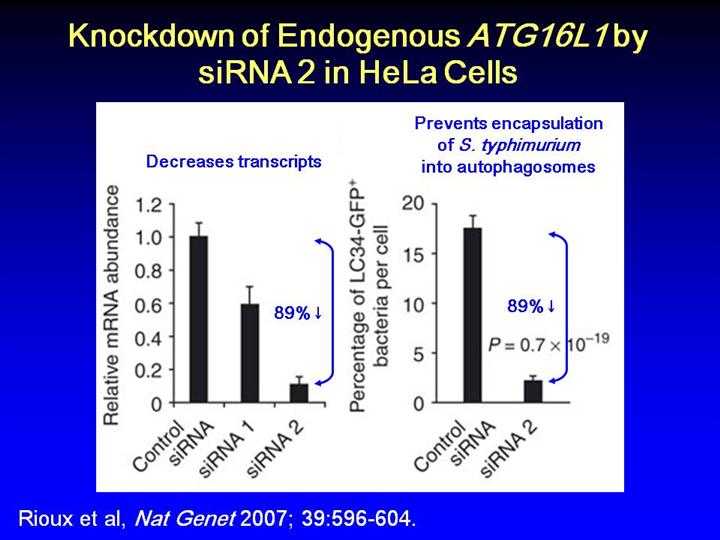 |
(b) Endogenous ATG16L1 mRNA knockdown (mean relative abundance s.d.) by siRNA 2 in HeLa cells within 48 h of transfection, as assessed by real-time quantitative RT-PCR normalized to GAPDH. Compared with control duplex, siRNA 2 yielded an 89% reduction in transcripts. RT-PCR was performed in triplicate; results represent two independent experiments. (c) Knockdown of ATG16L1 prevented effective autophagy of S. typhimurium in HeLa cells. Forty-eight hours after cotransfection with control siRNA or duplex 2 and LC3-GFP plasmid, HeLa cells were infected for 1 h with Salmonella typhimurium SL1344, fixed and examined microscopically. Mean percentages ( s.e.m.) of bacteria per cell encapsulated by LC3+ membranes (autophagosomes) are shown. Bacterial counts were pooled from two separate experiments; each counted a minimum of 100 infected cells. Significance was assessed by two-tailed Students t-test, assuming unequal variances.
|