| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35|36 |37 |38 |39 |40 |41 |42 |43 |44 |45 |46 |47 |48 |49 |50 |51 |52 |53 |54 |55 |56 |57 |58 |review |
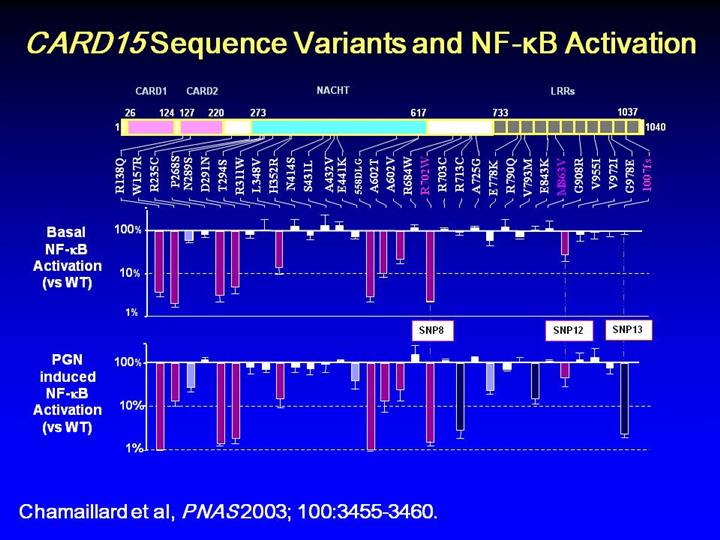 |
•The
candidate IBD1 gene has high expression in leukocytes and encodes a
1,013-aa protein identical to NOD2, an apoptosis regulator (of the
CED4/A_AF1 superfamily). The C-terminal leucine-rich region has binding
activity for bacterial lipopolysaccharides and its deletion stimulates
NF-kB activation. NF-kB is activated by inflammatory stimuli such as
cytokines and bacterial or viral products. Inappropriate activation has
been linked to inflammatory events associated with numerous autoimmune
and inflammatory diseases, while inhibition of NF-kB has been linked to
apoptosis.
•Three
independent associations were demonstrated with SNPs 8, 12, and 13;
their rare alleles were never found on the same haplotype and associated
with different alleles of D16S3136, explaining the original conflicting
associations with this marker. The IBD1/NOD2 gene, which was renamed
CARD15 due to the two caspase-recruitment domains at its N-terminal, was
demonstrated through functional assays to activate the NF-kB pathway in
vitro in response to various baterial components. This provided a
functional assay which would permit testing of bacterial peptidoglycan
response in cells transfected with CARD15 variants.
•As
seen in panel A, SNPs 8 and 12 had impaired basal NF-kB activation
compared to wild type, as did several other SNPs carried by Crohn’s
disease patients. SNPs 8, 12, and 13 had impaired induced activation as
shown in Panel B. Quantitative parametrization of this response,
estimated from the patients' CARD15 genotypes, was associated with
several clinical manifestations of Crohn’s disease.
•Prototype
I: variants indistinguishable from wildtype (white/white)
•Prototype
2:
2-fold reduction in both basal activity and PGN-induced
response, indicating a constitutive defect of CARD15 function
(gray/pink)
•Prototype
3: almost unchanged basal activity (at least 80% residual activity), but
a major impairment of the PGN-response (20% that of WT), thus
demonstrating a specific defect in PGNsensing caused by alteration in
the LRR domain. (black/dark blue)
•Cross-hatched=cyan=
intermediate 2 and 3
•The
availability of this functional assay provided strong experimental
evidence for a role of these three variants, and the protein produced by
CARD15, in Crohn’s disease.
|