GABAAR Membrane Trafficking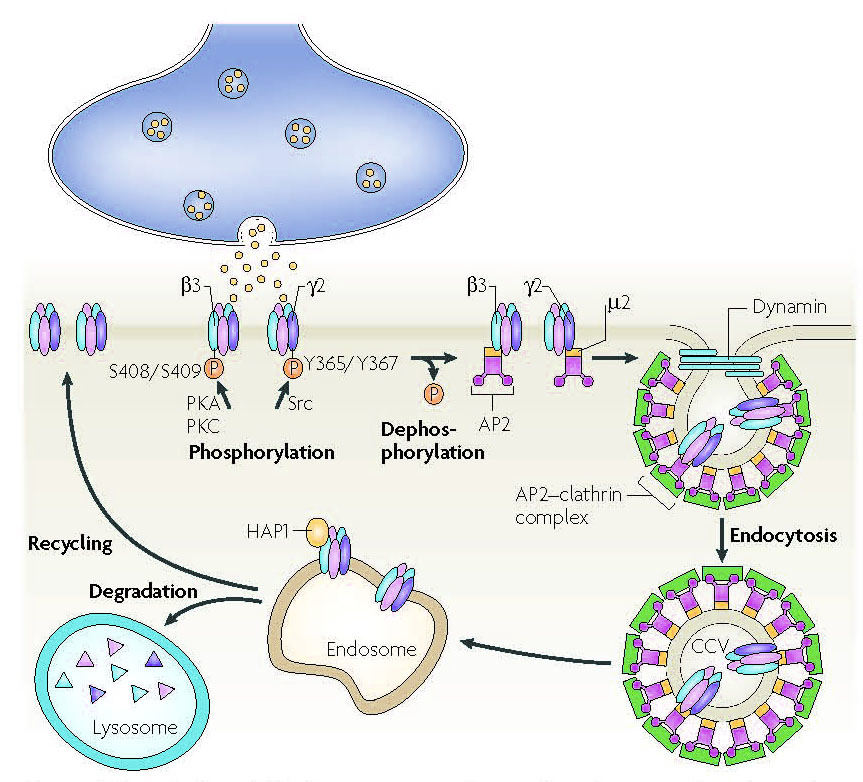
Jacob et al., Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2008 GABAAR are assembled in the ER, trafficked through the Golgi and segregated into vesicles which are inserted at extrasynaptic plasma membrane locations. Receptors diffuse laterally and are stabilized at synapses by scaffolding proteins. To be removed from the cell surface, GABAAR diffuse out of synapses and undergoing clathrin dependent endocytosis. At this step, receptors can be either recycled back to the cell surface via the endosome or degraded in the lysosome.These trafficking processes are extremely rapid and dynamic. Extrasynaptic receptors are highly mobile, while synaptic receptors are tethered and stabilized by gephyrin Lateral diffusion allows synaptic entry of receptors in minutes. And finally GABAAR undergo extensive endocytosis, with at least 25% of receptors being internalized in 20 minutes. Endocytosis Assay
Incorporation of an N-terminal pH-sensitive GFP reporter in GABAAR subunits allows the specific visualization of surface receptor subtypes in living neurons, while a bungarotoxin (Bgt) binding site (BBS) allows measurements of receptor insertion, removal and recycling with application of exogenous fluorescent Bgt in hippocampal neurons (see Fig.1). Dendritic Maturation and PlasticitySpine Elongation and Retraction Spine Dynamics |