|
 |
front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |review |
|
Search for most updated materials ↑
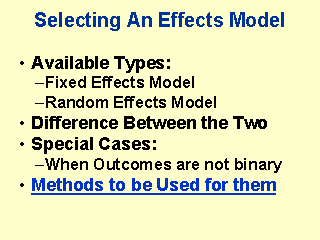
Random
Effects Model: Answers the question, on the basis of the studies that are
examined, is it possible to comment that the treatment or the exposure will
produce a result? A random effects model is computationally more intense than a fixed effects model.
Also, if the studies are homogeneous, fixed effects and random effects models are similar. In this tutorial, we will also examine special situations when the outcomes are on a
continuous scale, rather than discrete counting of events. Finally, check out this table about the methods to be used for different types of
models. |