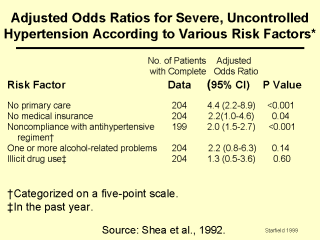
 |
*Adjustment
was made in each model for age, sex, race or ethnic group, educational level, and current
smoking status, but not for other risk factors. Odds ratios are expressed as the risk of
severe, uncontrolled hypertension for a patient with the risk without it. CI denotes
confidence interval.A
case-control study of visits by hypertensive men in one inner city hospital emergency room
compared those whose hypertension was controlled with those in whom the hypertension was
uncontrolled. After controlling for a variety of other related factors (such as race and
education), men whose hypertension was uncontrolled were over four times as likely to have
no primary care source as those whose hypertension was controlled. This was by far
the most salient correlate of hypertension control of the several factors that were
studied.
Source: Shea S, Misra D, Ehrlich MH, Field L, Francis CK.
Predisposing factors for severe, uncontrolled hypertension in an inner-city minority
population. N Engl J Med 1992; 327(11):776-781. |
