| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |review |
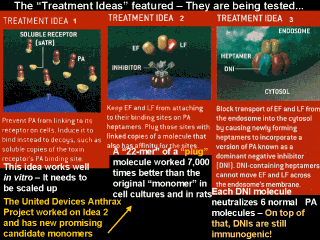 |
TREATMENT IDEA
1: Prevent PA from linking to its receptor on cells. Induce it to bind instead to
decoys, such as soluble copies of the toxin receptor's PA binding site. TREATMENT IDEA 2: Keep EF and LF from attaching to their binding sites on PA heptamers. Plug those sites with linked copies of a molecule that also has affinity for the sites. TREATMENT IDEA 3: Block transport of EF and LF from the endosome into the cytosol by causing newly forming heptamers to incorporate a version of PA known as a dominant negative inhibitor (DNI). DNI-containing heptamers cannot move EF and LF accross the endosome's membrane. |