 |
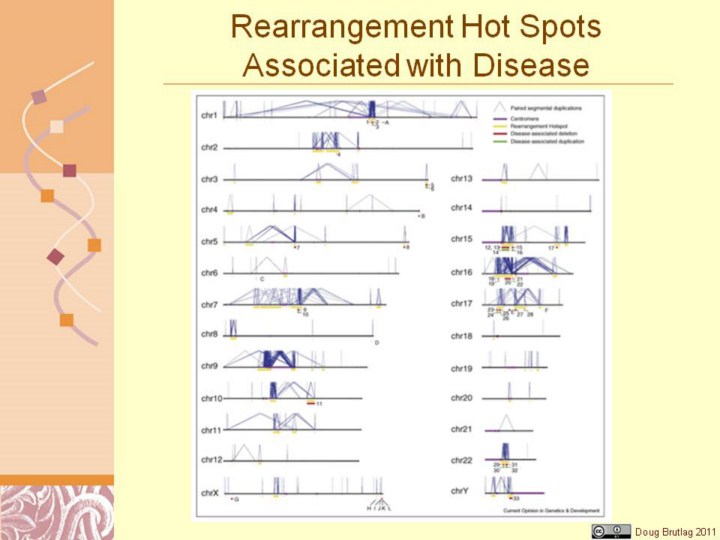
Rearrangement hotspots and their associated disease phenotypes. Each
chromosome is depicted as a horizontal line with intrachromosomal segmental
duplications connected by blue lines. Gold bars represent ‘rearrangement
hotspots’ defined as unique regions (50 kb–10 Mb) flanked by
intrachromosomal segmental duplications >10 kb with >95% sequence identity.
Disease-associated deletions and duplications are represented by red and
green bars, respectively. Numbers represent rearrangements within hotspot
regions as defined above: (1) TAR syndrome, (2) 1q21.1 deletion and (3)
reciprocal duplication, (4) juvenile nephronophthisis, (5) 3q29 deletion and
(6) reciprocal duplication, (7) spinal muscular atrophy, (8) Sotos syndrome,
(9) Williams syndrome and (10) reciprocal duplication, (11) 10q22–q23
microdeletion, (12) Prader–Willi syndrome, (13) Angelman syndrome, (14)
duplication 15q11, (15) 15q13.3 microdeletion and (16) reciprocal
duplication, (17) 15q24 microdeletion, (18) 16p13.11 deletion and (19)
reciprocal duplication, (20) 16p11.2–p12.2 deletion and (21) 16p11.2
deletion and (22) reciprocal duplication, (23) HNPP, (24) CMT1A, (25)
Smith–Magenis syndrome, (26) Potocki–Lupski syndrome, (27) renal cysts and
diabetes (RCAD) syndrome, (28) 17q21.31 microdeletion syndrome, (29)
velocardiofacial/DiGeorge/deletion 22q11 syndrome and (30) reciprocal
duplication, (31) distal 22q11.2 deletion and (32) reciprocal duplication,
and (33) azoospermia. Letters represent NAHR-mediated deletions that occur
outside of hotspots (as defined above): (A) Gaucher disease, (B)
fascioscapulohumeral dystrophy, (C) congenital adrenal hyperplasia, (D)
glucocorticoid-remediable aldosteronism, (E) neurfibromatosis type I
microdeletion syndrome, (F) pituitary dwarfism, (G) X-linked ichthyosis, (H)
Hunter syndrome, (I) red–green color-blindness, (J) Emery–Dreifuss muscular
dystrophy, (K) incontinentia pigmenti, and (L) hemophilia A.
|
