| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35 |36 |37 |38 |39 |40 |41 |42 |43 |44 |45 |46 |47 |48 |49 |50 |51 |52 |53 |54 |55 |56 |57 |58 |59 |60 |61 |review |
 |
http://www.genome.gov/
Finished Sequence in 2004 (Build 35)
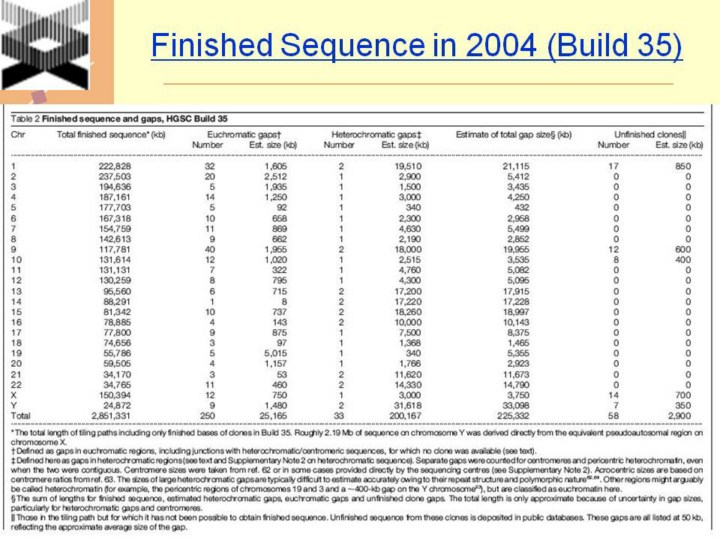
* The total length of tiling paths including only finished bases of clones in Build 35. Roughly 2.19 Mb of sequence on chromosome Y was derived directly from the equivalent pseudoautosomal region on chromosome X. † Defined as gaps in euchromatic regions, including junctions with heterochromatic/centromeric sequences, for which no clone was available (see text). ‡ Defined here as gaps in heterochromatic regions (see text and Supplementary Note 2 on heterochromatic sequence). Separate gaps were counted for centromeres and pericentric heterochromatin, even when the two were contiguous. Centromere sizes were taken from ref. 62 or in some cases provided directly by the sequencing centres (see Supplementary Note 2). Acrocentric sizes are based on centromere ratios from ref. 63. The sizes of large heterochromatic gaps are typically difficult to estimate accurately owing to their repeat structure and polymorphic nature62,64. Other regions might arguably be called heterochromatin (for example, the pericentric regions of chromosomes 19 and 3 and a ,400-kb gap on the Y chromosome23), but are classified as euchromatin here. § The sum of lengths for finished sequence, estimated heterochromatic gaps, euchromatic gaps and unfinished clone gaps. The total length is only approximate because of uncertainty in gap sizes, particularly for heterochromatic gaps and centromeres. k Those in the tiling path but for which it has not been possible to obtain finished sequence. Unfinished sequence from these clones is deposited in public databases. These gaps are all listed at 50 kb, reflecting the approximate average size of the gap. |