| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35|36 |37 |38 |39 |40 |41 |42 |43 |44 |45 |46 |47 |48 |49 |50 |51 |52 |53 |54 |55 |56 |57 |58 |59 |review |
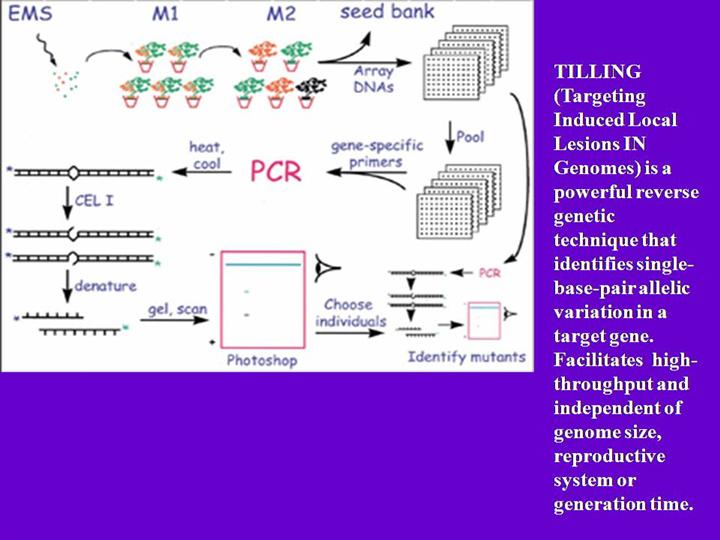 |
High-throughput TILLING (Henikoff S. 2001 ). Seeds are collected and mutagenizd with EMS.M1 plants are allowed to grow and self-pollinated to obtain M2 generations. Each M2 derives from a different M1 plant. M2 DNAs are prepared and M3 seeds are cataloged. To improve efficiency, DNA are pooled. Primers are designed and labeled with IR-dye. After PCR, heating and cool are performed to form mismatches which can be detected and cut by CEL1. Then denature, gel electrophoresis, and scanning with DNA analyzer. Once a single-base-pair allelic variation is screened, use bioinformatic methods and check phenotype. Then the gene function also will be deduced.
|