 |
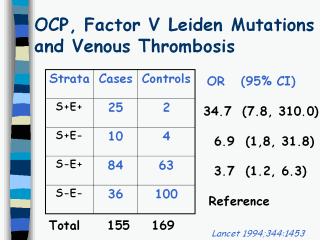
These data are presented in the cited
manuscript. Individuals who do not carry the mutation but have been exposed
to OCP have a ~4-fold increased risk of VT than those who do not carry the
mutation and were not exposed to OCP. Those who carry the mutation but have
not used OCP have a ~7-fold increased risk of VT compared to those do not
carry the mutation or used OCP. However, the risk for individuals with the
mutation and exposure to OCP is very high, ~35 times greater than the risk
for women with neither the mutation or exposure to OCP.
|
