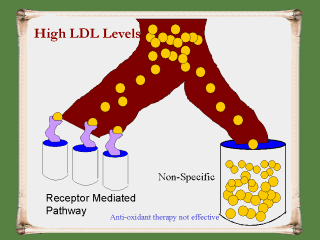
 |
In contrast to
vitamin E, HDL, apoA-I, and apoA-I mimetic peptides have been shown to
prevent LDL oxidation in cell-free systems and in the artery wall co culture
studies. HDL, apoA-I, and apoA-I mimetics have been shown to decrease
lesions and improve vascular reactivity in animal models of atherosclerosis
and in humans. HDL cholesterol promotes cholesterol efflux from extra
hepatic tissues and thus can reduce the transformation of macrophages into
foam cells and thus reduce fatty streak (foam cell)
|
