| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |review |
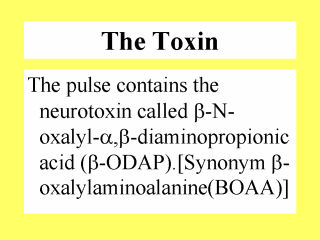 |
The toxin bring neuronal damage commonly to the motor cells of the thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves through its excitatoxic action on the glutamate receptors. Symmetrical axonal degeneration of both crossed and uncrossed pyramidal tracts in the spinal cord is the principal pathological change observed. |