| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |review |
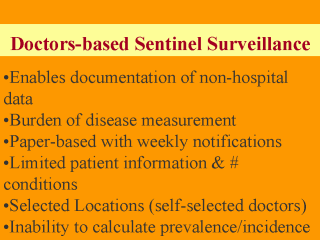 |
A computerised
sentinel surveillance system operating under the principle of extracting selected data
fields from doctorsí desktops. This would allow a selected number of practices participate in documentation of burden of disease (defined as number of consultation, new and follow-up cases, pharmacological therapy or psychoterapy, and referral to specialised services. Advantages: this usually provides data not available routinely outside hospital, does not require extra work from doctors, and ensures consistency of data gathered from different locations. Disadvantages: it requires consent from the patient and the participating doctors and training of doctors in the use of case definitions. Data transfer has to be encrypted. Cannot calculate prevalence as the representativeness of the sample of medical practices may not be extrapolated to the rest of the State or country. |