 |
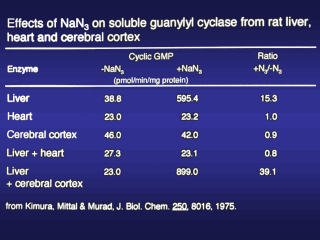
In our first
experiment we mixed crude supernatant fractions of rat liver that could be
activated with azide with fractions of rat brain and rat health, tissues
without azide effects on guanylyl cyclase. Mixing extracts of liver with
cerebral cortex resulted in an increased azide effect, while mixing liver
extracts with heart extracts resulted in a loss of the azide effect. Our
interpretation of these data was that azide activation required the presence
of other factors present in liver extracts that when added to cerebral
cortex permitted azide to activate the enzyme from both tissue extracts.
Furthermore, heart extracts possessed a factor(s) that blocked azide
activation in the heart extract and in liver extracts in the mixing
experiments.
|
