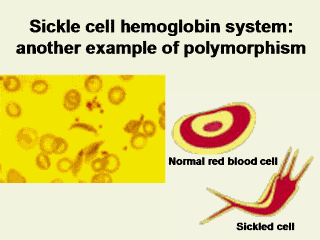
 |
In this, Hbs genes
may be lost from the population each time a homozygote (who has sickle cell
disease) fails to contribute to the next generation because of death before
the reproductive age. The heterozygotes (HBs/HBa) are, however, thought to
be differentially maintained in the population because individuals with this
phenotype are less likely to succumb to falciparum malaria and consequently
survive to contribute genes to the next generation. The theory implies that
there are different selective values to the several forms of polymorphisms.
|
