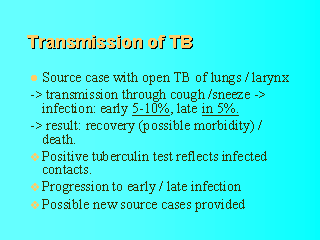
 |
Human
TB infection is almost exclusively due to M. tuberculosis, transmitted by airborne
droplet nuclei (size 1-5 m m) when somebody with active,
open TB of the lungs or larynx (source case) coughs, sneezes or sings.
Susceptible persons (contacts) who breathe air contaminated with these droplet nuclei can
develop (latent) TB infection. Infected contacts develop a positive delayed-type
hypersensitivity reaction to the tuberculin test between 2-10 weeks after initial
infection. 5-10% progress to active TB within the first 2 years of infection, another 5%
develop active TB (endogenous / exogenous) within their lifetime. |
