| front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35 |review |
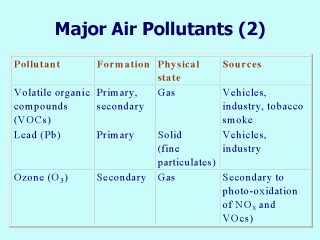 |
Volatile Organic
Compounds (VOCs) VOCs are a varied group of compounds present in the atmosphere, which include a wide range of hydrocarbons such as alkanes, alkenes, aromatics, aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, esters, and some chlorinated compounds. Benzene is an aromatic VOC which has received much attention due to its carcinogenicity. Other aromatic compounds such as toluene are important precursors of ozone. Lead (Pb) Emissions from motor vehicle are the main source of lead in air, principally present as particles with diameter less than 1 m m. In an important and increasing number of countries, lead emitted by vehicles is declining with the introduction of unleaded fuels. Photochemical Oxides They are pollutants resulting from chemical reactions between reactive hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides under the effect of solar light. Ozone (O3) is, from a toxicological point of view, the most important among these pollutants. Provided that vehicle-emission-generated primary pollutants react with it, it may be found in considerably large concentrations even in areas far apart from the sources of emission and its levels are frequently higher around big cities rather than inside. |