|
|
|
|
front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |review |
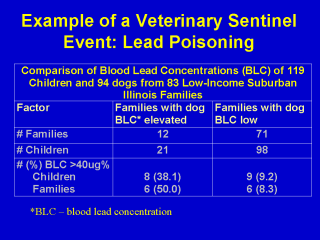 |
Demonstration of an elevated blood lead concentration (BLC) in a family dog increased the probability sixfold of finding a child in the same family with an elevated BLC.* Thirty-eight percent of families with dogs having an elevated BLC also had a child with an elevated BLC compared with only 9% of families with dogs having a low BLC. The clinical signs of acute lead toxicity in children and dogs are similar. *Thomas, CW., et. al. Blood lead concentrations of children and dogs from 83 Illinois families. J Amer Vet Assoc, 169(11):1237-40, 1976. |