Search inside of Supercourse and lectures in HTML and PPT format
 |
 |
front |1 |2 |3 |4 |5 |6 |7 |8 |9 |10 |11 |12 |13 |14 |15 |16 |17 |18 |19 |20 |21 |22 |23 |24 |25 |26 |27 |28 |29 |30 |31 |32 |33 |34 |35 |36 |37 |38 |39 |40 |41 |42 |43 |44 |45 |46 |47 |48 |49 |50 |51 |52 |53 |54 |55 |56 |57 |58 |59 |60 |61 |62 |review |
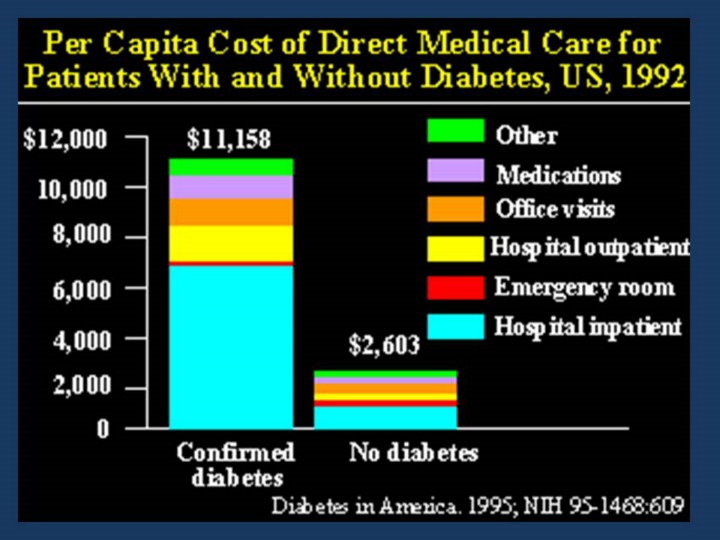 In the United States, as in many developed countries, the cost of caring for patients with diabetes is considerably higher than for those without. As can be seen, the per capita costs are about 3 to 4 times those of the non-diabetic population. Most of this increased cost is due to the complications, particularly those requiring hospitalizations. Seventy-five percent of hospitalizations are due to cardiovascular complications. |
|