| HPS 0410 | Einstein for Everyone | Spring 2007 |
Back to main course page
For submission Tuesday April 3, Wednesday April 4.
We can use Hubble's relation to arrive at a crude estimate of the age of the universe. That is, we will calculate how long ago all the galaxies were crammed into our neighborhood of space. This time will be our estimate of how long ago the big bang happened. We will assume that each galaxy has moved at a constant speed for all time, although this speed will vary from galaxy to galaxy.
We will use the value of 20 km/sec per 1,000,000 light-years for Hubble's constant.
1. (a) If a galaxy is 1,000,000 light-years away from us now, according to Hubble's relation, how fast is it receding from us?
(b) A galaxy traveling at 1 km/sec will travel one light-year in 300,000 years. How long does the galaxy of (a) require to travel a light-year?
(c) How long did it take the galaxy of (a) to get to its position 1,000,000 light-years distant from us?
2. Repeat the calculation of 1. for a galaxy now 2,000,000 light years distant from us.
3. Repeat the calculation of 1. for a galaxy now 3,000,000 light-years distant from us.
The final result of 1., 2., and 3. should be the same. At the time calculated, all the matter of universe would have been compressed into our neighborhood. This is our estimate of the age of the universe, often called the "Hubble age."
4. The dynamics that drive standard relativistic cosmologies are somewhat hard to understand. It turns out that this relativistic dynamics is mimicked in several important aspects by some simple dynamical systems in Newtonian theory. Those systems consist of a quantity of matter concentrated into a point in an empty Newtonian universe. That point explodes violently throwing out fragments of matter in all directions, producing an expanding cloud of debris. In Newtonian gravitation theory, every fragment of matter exerts an attractive gravitational force on every other fragment. These attractive forces act to pull the fragments of the cloud back together, slowing the rate of expansion of the cloud of debris.
There are three different types of histories for the cloud, according to the energy of the initial explosion:
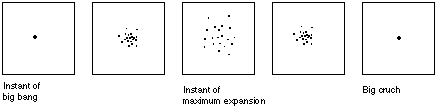
I. Low energy explosion. The energy of the explosion is not great enough to overcome the attractive forces of gravitation and the cloud collapses back onto itself under gravitational forces.

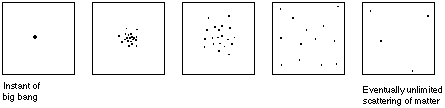
II. High energy explosion. The energy of the explosion is sufficient to overcome the attractive forces of gravitation. The fragments continue to move apart without limit. The cloud is spread more and more thinly over time and never collapses back to a point. Only a part of the total energy of the explosion is needed to overcome the attractive forces of gravitation. The remainder fuels a continuing rapid expansion.
III. Critical energy explosion. The energy of the explosion is the exact minimum needed to prevent recollapse. Over time all of the energy of the explosion is used up in counteracting the attractive forces of gravitation. The critical energy level lies exactly on the boundary between the energies of I. and II.
(a) Which Newtonian model is associated with which relativistic cosmology?
(b) While these Newtonian models are remarkably good in mimicking the relativistic dynamics, the Newtonian models differ from the relativistic cosmologies in several very important ways. What are they?
For discussion in the recitation.
A. Consider (0) our galaxy and galaxies (I) 1,000,000 and (II) 2,000,000, and (III) 3,000,000 and (IV) 4,000,000 light years distant from us, all in the same direction. Compute the velocities of recession of the galaxies (I)-(IV) from us.
Now imagine that you are an observer located on galaxy (I). Recompute the velocities of recession of the other galaxies. Find that the Hubble law still holds. That means that the expansion looks the same to all observers, no matter where they are located.
(In computing these velocities, use the ordinary Newtonian rule for composing velocities.)
B. Some theorists find a singularity, such as the big bang, an affront to science and feel a strong need to find reformulated theories that will eliminate them. Are singularities to be avoided or eliminated from theories if possible?
C. The red shift of light from distant galaxies has been interpreted almost universally as evidence of the galaxies velocity of recession. However other effects can produce red shifts, most notably, intense gravitational fields. Ought we to interpret the red shift differently, as some heterodox theorists have urged? How could we distinguish a red shift due to a velocity of recession from one due to an intense gravitational field?